
What is Accounting?
Accounting can be described as the process of recording financial transactions with the object of determining and interpreting profits. That means it is a particular type of processing method which gives us financial status of our company or organization, preparation of financial statements, audits, cost studies, income tax work and analysis and interpretation of accounting information for internal and external end-users as an aid to making business decisions.
Accounting can be described as the process of recording financial transactions with the object of determining and interpreting profits. That means it is a particular type of processing method which gives us financial status of our company or organization, preparation of financial statements, audits, cost studies, income tax work and analysis and interpretation of accounting information for internal and external end-users as an aid to making business decisions.
Functions of Accounting:
1. Keeping of a systematic and permanent record of monetary transactions with a view to help the preparation of Final Statements of Accounts.
2. Communication of results of the transactions recorded to various people like owners, creditors etc.
3. Fulfilling the legal requirements for taxation.
4. Helping in the protection of assets and property by recording correct and fair value.
Branches of Accounting:
Financial Accounting:-
Financial Accounting is art of recording, classifying and summarising financial transactions and preparing preparation of profit & loss account and balance sheet and also interpretation of financial statements.
● Cost Accounting:-
Cost Accounting is the branch of accounting which deals with the classification, recording, allocation, summarisation and reporting of current and prospective costs. It is the process of accounting for cost and helps the controlling of cost.
● Management Accounting:-
Management Accounting is process to supply of information which is useful to management in decision making for efficient running for the business and also for the maximisation profit. It covers such as cost accounting budgetary control, inventory control, capital budgeting, cost of capital, capital structure decisions, dividend decisions, internal audit etc.
Financial Accounting is art of recording, classifying and summarising financial transactions and preparing preparation of profit & loss account and balance sheet and also interpretation of financial statements.
● Cost Accounting:-
Cost Accounting is the branch of accounting which deals with the classification, recording, allocation, summarisation and reporting of current and prospective costs. It is the process of accounting for cost and helps the controlling of cost.
● Management Accounting:-
Management Accounting is process to supply of information which is useful to management in decision making for efficient running for the business and also for the maximisation profit. It covers such as cost accounting budgetary control, inventory control, capital budgeting, cost of capital, capital structure decisions, dividend decisions, internal audit etc.
Personal Accounts:
These types of account in which a trader’s dealing with persons or firms are recorded. e.g. Ram’s A/c, JK Enterprises, Outstanding etc. Outstanding is a personal account because it represents regarding person.
2. Impersonal Accounts:
These types of accounts are not concerned with any individual person of firm. It is divided in two categories.
a. Real Accounts:
It is also called Property Account which are recorded the dealings relating to property, e.g. Stock A/c, Furniture A/c, Investment A/c etc.
b. Nominal Accounts:
These types of account are those in which a trade’s dealings relating to expenses, losses or gains and income are recorded, e.g. Rent A/c, Salary A/c, Discount A/c etc.
Double entry system:
The double entry system is based on scientific principles and is, therefore, used by most of the business places. The system recognizes the fact that every transaction has two aspects and records both aspects of each and every transaction. Under it every transaction an account is debited and some other account is credited.
Features of Double Entry System of Book Keeping
These types of account in which a trader’s dealing with persons or firms are recorded. e.g. Ram’s A/c, JK Enterprises, Outstanding etc. Outstanding is a personal account because it represents regarding person.
2. Impersonal Accounts:
These types of accounts are not concerned with any individual person of firm. It is divided in two categories.
a. Real Accounts:
It is also called Property Account which are recorded the dealings relating to property, e.g. Stock A/c, Furniture A/c, Investment A/c etc.
b. Nominal Accounts:
These types of account are those in which a trade’s dealings relating to expenses, losses or gains and income are recorded, e.g. Rent A/c, Salary A/c, Discount A/c etc.
Double entry system:
The double entry system is based on scientific principles and is, therefore, used by most of the business places. The system recognizes the fact that every transaction has two aspects and records both aspects of each and every transaction. Under it every transaction an account is debited and some other account is credited.
Features of Double Entry System of Book Keeping
● Each transaction has two aspects, i.e., debit and credit
● Maintains a complete record of all business transactions
● Helps to check the accuracy of the accounting transactions, by preparation of trial balance
● Helps ascertaining profit earned or loss occurred during a period, by preparation of Profit & Loss Account
● Helps ascertaining financial position of the concern at the end of each period, by preparation of Balance Sheet
● Helps timely decision making based on sufficient information
● Minimises the possibilities of fraud due to its systematic and scientific recording of business transactions.
There are three basic rules for recording transactions.
I. Debit the Receiver while Credit the Giver.(Personal A/c)
II. Debit what comes in while credit what gores out.(Real A/c)
III. Debit all expenses and losses while Credit all incomes and gains.(Nominal A/c)
The journal is the book in which all business transactions are recorded as per the rules of double entry system. It is that particular type of technique by which we can record day by day transaction entries.
The Performa of Journal is as :
The Performa of Journal is as :
Ledger is set of accounts which contains a classified and permanent record of all transactions of a business.
The Performa of Journal is as :
The Performa of Journal is as :
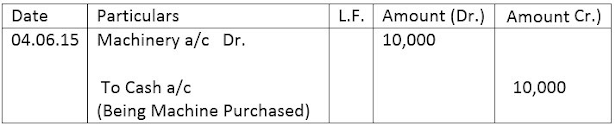
Posting is the process of transferring the debit and credit items from journal to classified accounts in the ledger. The main function of the posting is to make classified and summarized record of each account in respect of various transactions that affect accounts.
Ex.- June 4, 2015 Purchased Machinery for Rs. 10,000.
Balancing is the process of equalizing the two sides of a account. Each account in the ledger receives both debit and credit entries at some times.
If total amount of debit is greater than total amount of credit is DEBIT BALANCE and total amount on credit side is more than the total amount on debit side is CREDIT BALANCE. The balance is put on the side of the account which is smaller by giving a reference of balance using Carried Forward (c/f or c/d) to the next period. On the other hand, the balance is brought forward and Brought Down (b/f or b/d) from the previous period while reopening an account in the next period.
Example:
If total amount of debit is greater than total amount of credit is DEBIT BALANCE and total amount on credit side is more than the total amount on debit side is CREDIT BALANCE. The balance is put on the side of the account which is smaller by giving a reference of balance using Carried Forward (c/f or c/d) to the next period. On the other hand, the balance is brought forward and Brought Down (b/f or b/d) from the previous period while reopening an account in the next period.
Example:
It is a statement not an account, it is a particular type of method which gives summarised information of ledgers, arithmetical accuracy, preparation of financial statement and comparing. The balance or total of debit must be equal to sum of the balance or total of credit.
It is divided in two categories.
1. Total Method: The total of debit and credit of the account are shown in Trial Balance. This method is rarely used.
2. Balance Method: The difference of each account is taken out. If the debit side of an account is greater than the credit side the difference is put in the debit column of the Trail Balance. If the credit side of an account is greater than the debit side the difference is put in the credit column of the Trail Balance.
The following rules may be used for T/B.
It is divided in two categories.
1. Total Method: The total of debit and credit of the account are shown in Trial Balance. This method is rarely used.
2. Balance Method: The difference of each account is taken out. If the debit side of an account is greater than the credit side the difference is put in the debit column of the Trail Balance. If the credit side of an account is greater than the debit side the difference is put in the credit column of the Trail Balance.
The following rules may be used for T/B.
| Debit Balances | Assets, Sundry Debtors, Drawings, Losses and Expenses. |
| Credit Balances | Liabilities, Sundry Creditors, Capital, Income & Gains. |
Profit and Loss Account Financial statements are final result of accounting work done during the accounting period. Financial statement serves a significant purpose to users of accounting information in knowing about the profitability and financial position of the organisation. Financial statements normally include
● Trading
● Profit and Loss Account
● Balance Sheet
Trading Account:
Trading refers to buying and selling of goods. The trading account displays the transactions per-training to buying and selling of goods. The difference between the two sides of the Trading Account indicates either Gross Profit or Gross Loss. If the credit side total is in excess of the debit side total, the difference represents Gross Profit. On the other hand, if the total of the debit side is in excess of the credit side total, the difference represents Gross Loss. Such Gross Profit / Gross Loss is transferred to Profit & Loss Account.
The Gross Profit is expressed as :
Profit and Loss Account:
The profit and loss account helps to ascertain the net profit earned or net loss suffered during a particular period. After considering all other incomes and expenses incurred over a period. This helps the company to monitor and control the costs incurred and improve its efficiency. In other words, the profit and loss statement shows the performance of the company in terms of profits or losses over a specified period.
The Net Profit is expressed as:
A key element of the Profit and Loss Account, and one that distinguishes it from a balance sheet, is that the amounts shown on the statement represent transactions over a period of time, while the items represented on the balance sheet show information as on a specific date.
Balance Sheet:
The balance sheet is a statement that summarises the assets and liabilities of a business. The excess of assets over liabilities is the net worth of a business. The balance sheet provides information that helps in assessing company’s Long-term financial strength, day-to-day working capital management.
The balance sheet is a statement that summarises the assets and liabilities of a business. The excess of assets over liabilities is the net worth of a business. The balance sheet provides information that helps in assessing company’s Long-term financial strength, day-to-day working capital management.
The balance sheet is a statement that summarises the assets and liabilities of a business. The excess of assets over liabilities is the net worth of a business. Horizontal Balance Sheet with Percentage/Working Capital Go to Gateway of Tally --> Balance Sheet --> press F12 and set 'Show Percentages' and 'Show Working Capital figures' to 'Yes' > press Alt+F1
Comparative Balance Sheet – Monthly
In detailed Balance Sheet, press F2 and change period from 1-2-2015 to 28-2-2015 > press C:
New Column> button (Alt+C) and set period from 1-2-2015 to 28-2-2015 for comparison.




















0 Comments